News
2025-07-10 18:06:48 Views:1019
A Powerful Tool in Common Bile Duct Stone Removal Surgery — The Mobile Flat-Panel C-Arm For Intervention
ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) is a minimally invasive procedure that combines X-ray imaging with endoscopy. Due to its advantages—such as minimal trauma, fast recovery, and fewer complications—ERCP is widely used for the diagnosis and treatment of pancreaticobiliary diseases.
The mobile flat-panel C-arm by Perlove Medical has become an indispensable tool for many medical institutions in assisting ERCP procedures, thanks to its exceptional imaging capabilities and operational flexibility.
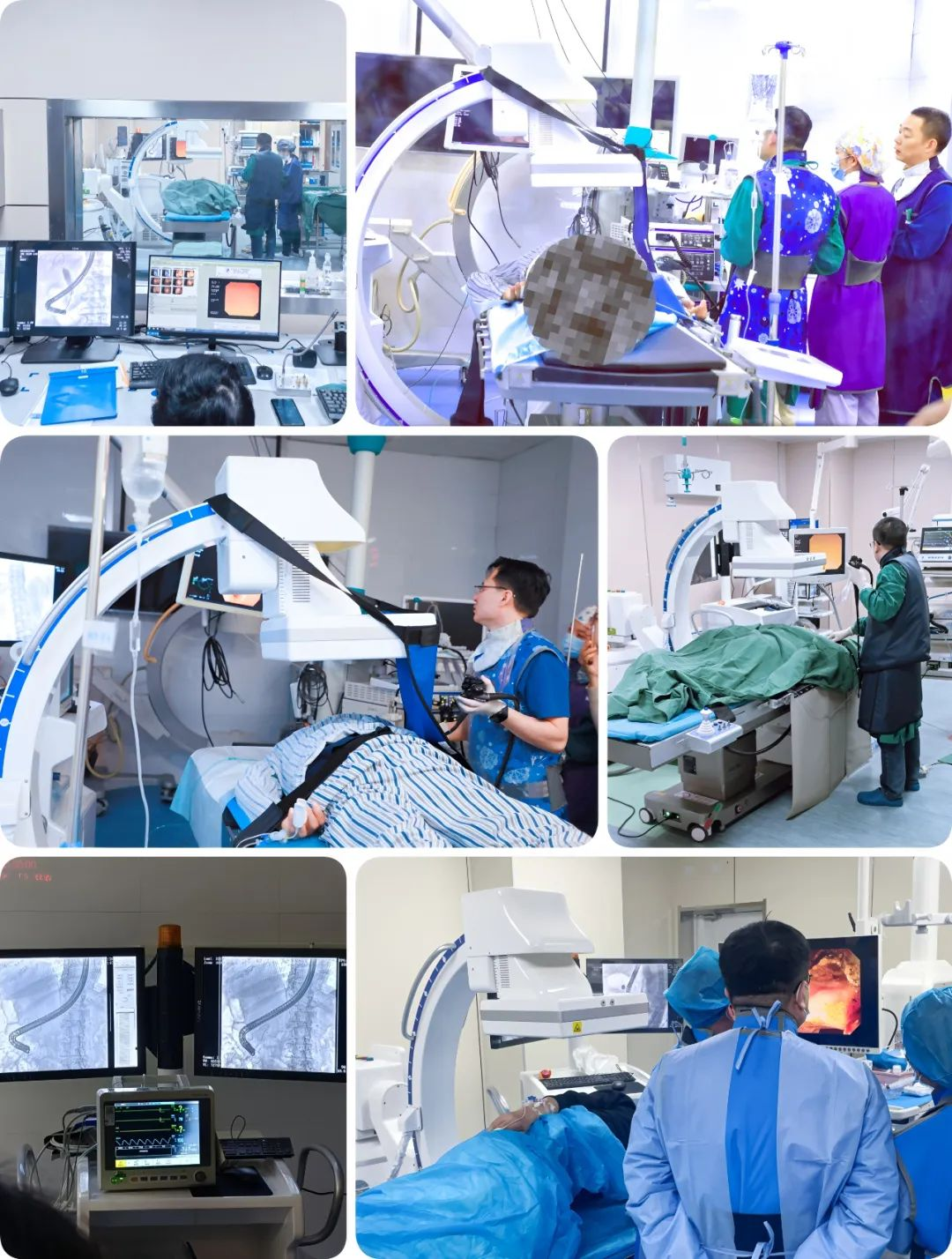
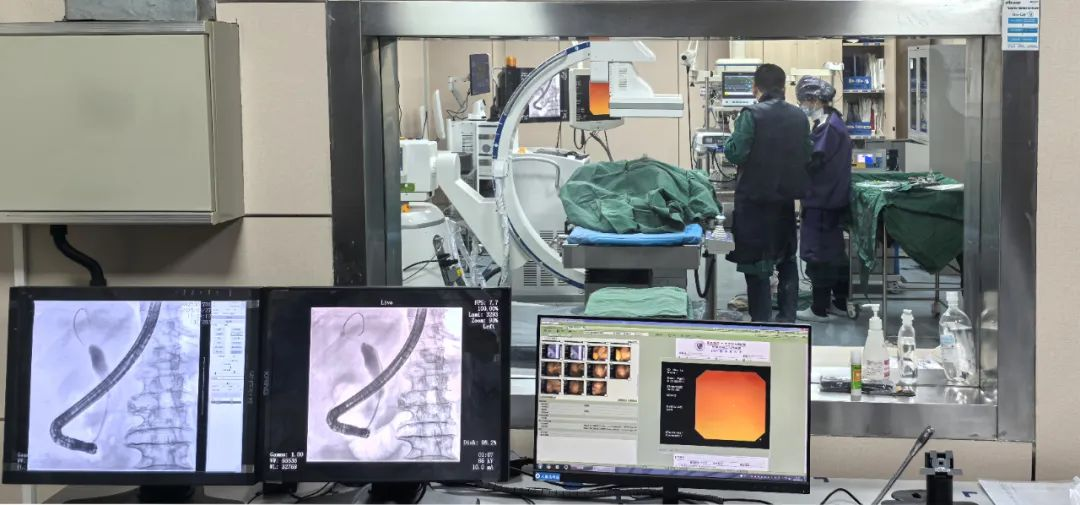
Mobile Flat-Panel C-arm for Intervention
Assisted choledochotomy procedure
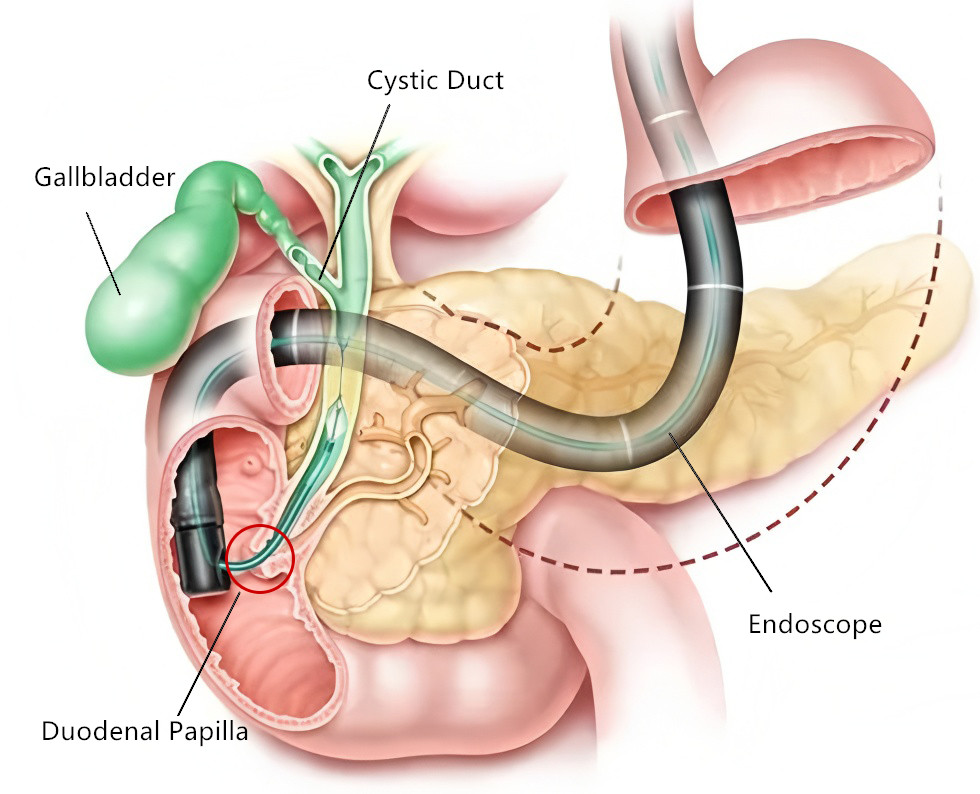
(Illustration of Common Bile Duct Stone Extraction Procedure)
Preoperative Preparation
1.Patient Evaluation
Conduct a comprehensive preoperative assessment, including medical history, symptoms, laboratory tests (e.g., liver function, blood count, amylase), and imaging studies (e.g., abdominal ultrasound, CT, MRCP).
Confirm the presence, size, location, and number of common bile duct (CBD) stones.
2.Equipment Preparation
Prepare the required instruments: X-ray equipment (Perlove Medical mobile flat-panel C-arm for intervention), duodenoscope, guidewire, catheter, contrast agent, stone retrieval basket, etc.
3.Patient Positioning
Typically, the patient is placed in a prone or left lateral position.
Intraoperative Procedure
1.Endoscope Insertion and Positioning
Under general anesthesia or sedation, insert the duodenoscope through the patient’s mouth, esophagus, and stomach into the descending part of the duodenum. Locate the duodenal papilla.
Duodenal papilla under endoscopic view.
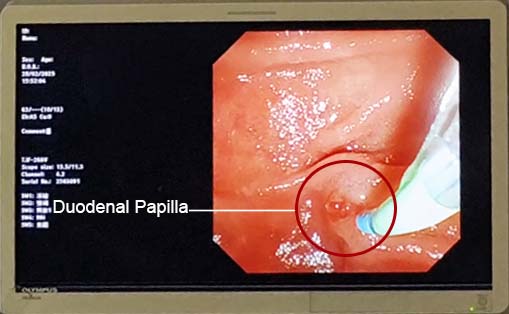
(Duodenal Papilla under Endoscopic View)
2. Catheter and Guidewire Insertion with Contrast Imaging
Under guidewire guidance, the catheter is inserted through the duodenal papilla into the common bile duct.
Contrast agent is injected into the bile duct, and provides real-time fluoroscopic visualization of the biliary anatomy, confirming the location, size, and number of stones.
3.Papillotomy or Dilation
The papilla is incised to enlarge the biliary orifice, facilitating stone extraction. For larger stones or cases where papillotomy is challenging, balloon dilation may be employed as an alternative.
4.Stone Extraction
Insert a stone retrieval basket into the bile duct to capture and extract the stones.
For larger stones, use a mechanical lithotripter to break them into smaller pieces before removal.
Use a balloon catheter to flush the bile duct, ensuring no residual stones remain.
5.Intraoperative Confirmation
Repeat cholangiography under the mobile flat-panel interventional C-arm to verify that the bile duct is free of residual stones.
6. Biliary Drainage
Following stone extraction, a nasobiliary drainage tube (ENBD) or biliary stent is routinely placed to maintain bile drainage, preventing cholangitis and biliary strictures..
With 22 years of dedication to medical imaging, Perlove Medical has accumulated extensive expertise in medical imaging technology and clinical services. The exceptional imaging quality of Perlove Medical clearly displays the fine structures of the biliary tract, assisting physicians in precisely locating calculi within complex anatomical environments. Meanwhile, the mobile design of the device eliminates the need for operating room modifications, offering flexible operation and ensuring smooth, efficient ERCP procedures. This delivers a safer, more efficient, and more comfortable diagnostic and therapeutic experience for patients
-
Perlove Medical at ECR 2026: Showcasing Cutting-Edge Imaging Solutions in Vienna
Read More » -
🌍 Elevating Global Healthcare | WHX Dubai 2026 Successfully Concluded
Read More » -
Join Us at ARAB HEALTH 2026 | See You in Dubai
Read More » -
Surgical Robots Take the Stage in the “Battle to Protect the Spine”
Read More » -
Application of 3D C-arm Imaging in Radiofrequency Ablation Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Read More » -
Correcting Limb Length Discrepancy | 3D C-arm Assisted Epiphysiodesis in Pediatric and Adolescent Patients
Read More »





